- Home
- HTML
-
CSS
- Introduction of CSS
- CSS Syntax
- CSS Selectors
- How To Add CSS
- CSS Comments
- CSS Colors
- CSS Backgrounds
- CSS Borders
- CSS Margins
- CSS Text
- CSS Lists
- CSS Tables
- CSS Box Model
- CSS Dimension
- CSS Padding
- CSS Border
- CSS Margin
- CSS Outline
- CSS Cursors
- CSS Overflow
- CSS Units
- CSS Visual Formatting
- CSS Display
- CSS Visibility
- CSS Position
- CSS Layers
- CSS Float
- CSS Alignment
- CSS Pseudo-classes
- CSS Pseudo-elements
- CSS Media Types
- CSS Sprites
- CSS Opacity
- CSS Attribute Selectors
- CSS Validation
- CSS3 Border
- CSS3 Gradients
- CSS3 Text Overflow
-
JavaScript
- JS Introduction
- JS Getting Started
- JS Syntax
- JS Variables
- JS Generating Output
- JS Data Types
- JS Operators
- JS Events
- JS Strings
- JS Numbers
- JS If Else
- JS Switch Case
- JS Arrays
- JS Sorting Arrays
- JS Loops
- JS Functions
- JS Objects
- JS DOM Nodes
- JS DOM Selectors
- JS DOM Styling
- JS DOM Get Set Attributes
- JS DOM Manipulation
- JS DOM Navigation
- JS Window
- JS Screen
- JS Location
- JS History
- JS Navigator
- JS Dialog Boxes
- JS Timers
- JS Date and Time
- JS Math Operations
- JS Type Conversions
- JS Event Listeners
- JS Event Propagation
- JS Borrowing Methods
- JS Hoisting Behavior
- JS Closures
- JS Strict Mode
- JS JSON Parsing
- JS Error Handling
- JS Regular Expressions
- JS Form Validation
- JS Cookies
- JS AJAX Requests
- JS ES6 Features
-
jQuery
- jQuery Introduction
- jQuery Syntax
- jQuery Selectors
- jQuery Events
- jQuery Show/Hide
- jQuery Fade
- jQuery Slide
- jQuery Animation
- jQuery Stop
- jQuery Chaining
- jQuery Callback
- jQuery Get/Set
- jQuery Insert
- jQuery Remove
- jQuery CSS Classes
- jQuery Style Properties
- jQuery Dimensions
- jQuery Traversing
- jQuery Ancestors
- jQuery Descendants
- jQuery Siblings
- jQuery Filtering
- jQuery Ajax
- jQuery Load
- jQuery Get/Post
- jQuery No-Conflict
-
PHP
- PHP Introduction
- PHP Install
- PHP Syntax
- PHP Comments
- PHP Variables
- PHP Echo / Print
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Strings
- PHP Constants
- PHP Operators
- PHP If...Else...Elseif
- PHP Switch
- PHP Loops
- PHP Functions
- PHP Arrays
- PHP Superglobals
- PHP Date and Time
- PHP Include
- PHP File Handling
- PHP File Upload
- PHP Cookies
- PHP Sessions
- PHP Filters
- PHP Callback Functions
- PHP JSON
- PHP Exceptions
- PHP What is OOP
- PHP Classes/Objects
- PHP Constructor
- PHP Destructor
- PHP Access Modifiers
- PHP Inheritance
- PHP Abstract Classes
- PHP Interfaces
- PHP Traits
- PHP Static Methods
- PHP Namespaces
-
SQL
- Introduction to SQL
- SQL Create Command
- SQL ALTER Command
- SQL Truncate Drop Rename
- INSERT SQL command
- UPDATE SQL command
- DELETE SQL command
- SQL COMMIT command
- SQL ROLLBACK command
- SQL GRANT and REVOKE Command
- SQL WHERE clause
- SQL LIKE clause
- SQL ORDER BY Clause
- SQL Group By Clause
- SQL HAVING Clause
- SQL DISTINCT keyword
- SQL AND OR operator
- SQL Constraints
- SQL Functions
- SQL JOIN
-
Python
- Getting started with Python
- Introduction to IDLE
- Python 2.x vs. Python 3.x
- Syntax Rules and First Program
- Numbers and Math Functions
- Python Operators
- Python Variables
- Python Modules and Functions
- Python Input and Output
- Data Types in Python
- String in Python
- String Functions in python
- Lists in Python
- Utilizing List Elements by Iterating
- Deleting List Elements & other Functions
- Dictionaries in Python
- Functions for Dictionary
- Tuples in Python
- Relational and Logical Operators
- Conditional Statements in Python
- Looping in Python
- Define Functions in Python
- Python-Introduction to OOP
- Object Oriented Programming in Python
- Classes in Python
- The concept of Constructor
- Destructors - Destroying the Object in Python
- Inheritance in Python
- Access Modifers in Python
- Types of Inheritance
- Method Overriding in Python
- Polymorphism
- static Keyword
- Operator Overloading Python
- Introduction to Error Handling
- Exception Handling: try and except
- Exeption Handling: finally
- Exception Handling: raise
- File Handling
- Reading and Writing File
- Introduction to Multithreading
- Threading Module in Python
- Thread Object
- Lock Object
- RLock Object
- Event Object
- Timer Object
- Condition Object
- Barrier Object
- __name__ Variable in Python
- Iterable and Iterator
- yield Keyword
- Python Generators
- Python Closures
- Python Decorators
- @property Decorator in Python
- Assert Statement
- Garbage Collection
- Shallow and Deep Copy
- Introduction to Logging
- Configure Log LEVEL, Format etc
- Python Logging in a file
- Python Logging Variable Data
- Python Logging Classes and Functions
- Python MySQL Introduction
- Create Database - Python MySQL
- Create Table - Python MySQL
- Insert Data in Table
- Select Data from Table
- Update data in Table
- Delete data from Table
- Drop Table from Database
- WHERE clause - Python MySQL
- Order By clause - Python MySQL
- Limit clause - Python MySQL
- Table Joins - Python MySQL
-
MongoDB
- MongoDB Introduction
- Overview of MongoDB
- MongoDB vs SQL Databases
- Advantages of MongoDB
- When to go for MongoDB
- Data Modelling in MongoDB
- Is MongoDB really Schemaless?
- Installing MongoDB on Windows and Linux
- Datatypes in MongoDB
- Create and Drop Database in MongoDB
- MongoDB: Creating a Collection
- CRUD Operations in MongoDB
- Data Relationships in MongoDB
- Indexing in MongoDB
- Sorting in MongoDB
- Aggregation in MongoDB
- Data Backup and Restoration in MongoDB
- Sharding in MongoDB
- Java Integration with MongoDB
-
Elixir
- Elixir Overview
- Elixir Environment
- Elixir Basic Syntax
- Elixir Data Types
- Elixir Variables
- Elixir Operators
- Elixir Pattern Matching
- Elixir Decision Making
- Elixir Strings
- Elixir Char Lists
- Elixir Lists and Tuples
- Elixir Keyword Lists
- Elixir Maps
- Elixir Modules
- Elixir Aliases
- Elixir Functions
- Elixir Recursion
- Elixir Loops
- Elixir Enumerables
- Elixir Streams
- Elixir Structs
- Elixir Protocols
- Elixir File I/O
- Elixir Processes
- Elixir Sigils
- Elixir Comprehensions
- Elixir Typespecs
- Elixir Behaviours
- Elixir Errors Handling
- Elixir Macros
- Elixir Libraries
-
TypeScript
- TypeScript Overview
- Install TypeScript
- First TypeScript Program
- Type Annotation
- TypeScript Variable
- TypeScript Data Type Number
- TypeScript Data Type String
- TypeScript Data Type Boolean
- TypeScript Arrays
- TypeScript Tuples
- TypeScript Enum
- TypeScript Union
- TypeScript Any Data Type
- TypeScript Void Data Type
- TypeScript Never Data Type
PHP Loops
This tutorial enables you to learn how to use PHP Loops. So, let us begin.
What is PHP Loop?
You can execute something over and over again by using the loop.
For example, for displaying all the numbers from 1 to 1000, you can just use a loop instead of using an echo statement 1000 times or specifying all the numbers in a single echo statement with newline character n. This is because a loop will run for 1000 times, and every time a number is displayed, starting from 1, the number is incremented after each iteration or cycle.
In a Loop, you either specify a condition or a LIMIT up till which the loop will execute, the reason being if such a condition is not specified, then it would be difficult to specify when the loop should end and not run for infinite time.
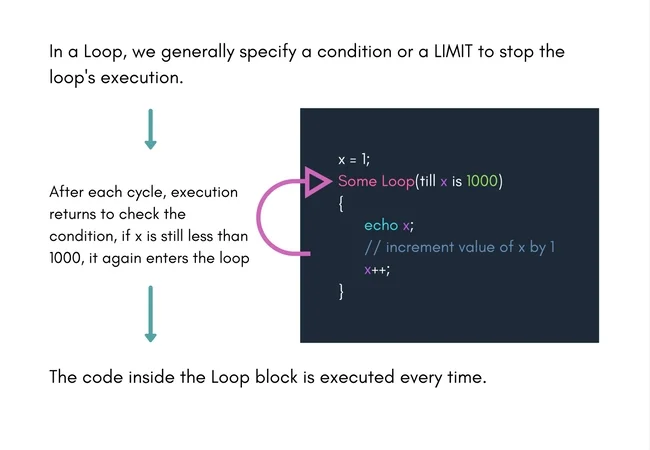
PHP while Loop
There are two components of the while loop in PHP. These are the condition and the code to be executed. The PHP while loop will execute the given code until the specified condition is true.
Syntax:
<?php
while(condition) {
/* execute this code till the condition is true */
}
?>
Example:
<?php
$a = 1;
while($a <= 10)
{
echo "$a | ";
$a++; // incrementing value of a by 1
}
?>Output:
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
PHP do...while Loop
It is a little different from all the loops in PHP. The reason is PHP do...while loop will execute at least one time, even in case the condition is false. Do you know how? Well, because it will check the condition after the loop's execution. Hence, the loop has already been executed once when the condition is checked.
Syntax:
<?php
do {
/* execute this code till the condition is true */
} while(condition)
?>
Example:
<?php
$a = 1;
do {
echo "$a | ";
$a++; // incrementing value of a by 1
} while($a <= 10)
?>Output:
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
Let us consider another example where the loop will be executed once even if the condition is false.
<?php
$a = 11;
do {
echo $a;
$a++; // incrementing value of a by 1
} while($a <= 10)
?>Output:
11As we can see, the condition in the above do...while loop example will return false because the $a variable's value is 11. So, according to the condition, the loop should be executed only if $a's value is less than or equal to 10.
PHP for Loop
The PHP for loop works differently from while or do...while loop. In for loop case, we have to declare beforehand how many times we want the loop to run.
Syntax:
<?php
for(initialization; condition; increment/decrement)
{
/* execute this code till the condition is true */
}
?>
The meaning of for parameters used is as follows:
- initialization: In it, a variable is initialized with some value- the variable acts as the loop counter.
- condition: The condition which is checked after each iteration/cycle of the loop is defined here. The loop is executed only in case the condition returns true.
- increment/decrement: The loop counter is incremented or decremented as per the requirements.
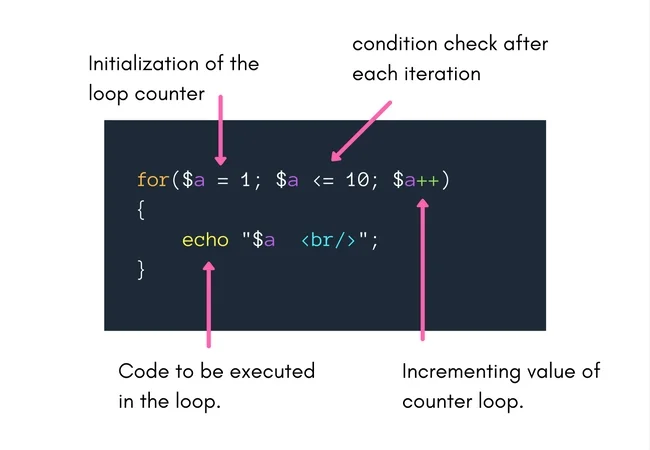
So, let us try printing numbers from 1 to 10 using the for loop.
<?php
for($a = 1; $a <= 10; $a++)
{
echo "$a <br/>";
}
?>Output:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Nested for Loops
A for loop can also be used inside another for loop. Here is a simple example of nested for loops.
<?php
for($a = 0; $a <= 2; $a++)
{
for($b = 0; $b <= 2; $b++)
{
echo "$b $a ";
}
}
?>Output:
0 0
1 0
2 0
0 1
1 1
2 1
0 2
1 2
2 2
PHP foreach Loop
You can use the foreach loop in PHP to access an array's key-value pairs. The foreach loop only works with arrays. You do not have to initialize any loop counter or set any condition for exiting from the loop; the loop does everything implicitly(internally).
Syntax:
<?php
foreach($array as $var) {
/* execute this code for all the array elements
$var will represent all the array
elements starting from first element, one by one */
}
?>
Example:
<?php
$array = array("Jaguar", "Audi", "Mercedes", "BMW");
foreach($array as $var)
{
echo "$var <br/>";
}
?>Output:
Jaguar
Audi
Mercedes
BMW
