Object Oriented Programming in Python
Welcome to another tutorial, here you will be introduced to the various concept of OOP in Python. In the previous tutorial, you were already introduced to class, inheritance, objects, and so on.
Objects
An object can be described as a physical entity, while a class is a logical definition. Although this has been discussed in previous tutorials. An object can be referred to as things like a car in a manufacturer's car database, or a pen in a stationary item management program. We have three important characteristics by which an object is identified. They include:
- Identity: This refers to a few pieces of information that can be used to identify the object of a class. This can be the name of the student, the car company name, and so on.
- Properties: In this case, the attributes of that object are called properties. That is the age, DOB, and gender of a student; the number of tires for a car, and so on.
- Behavior: for any object, its behavior is equivalent to the functions it can perform. Also, in OOP, you can assign some functions to objects of a class.
Class
We have already explained what a class is. It is a blueprint where attributes and behavior are defined. E.g. if Yarsi. Gilja, you are objects, then a human being is a class.
In addition, an object is the fundamental concept of OOP, however, classes are responsible for providing an ability to define the similar type of objects.
For any class, the data and functions that are operating on the data are bundled as a unit.
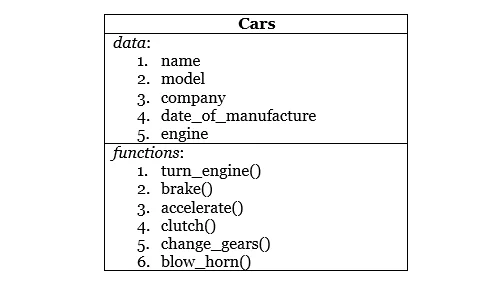
For illustration purposes, say there is a class named Car, that has few basic data such as name, model, brand, date of manufacture, engine number, and so on, with some functions such as turning the engine on, applying brakes, accelerating, change gear, and so on.
After the basic features have been defined in our class Car, then an object can be created by setting values for properties name, model, company, and so on, and the object of the class Car will be able to use the functions defined in it.
Data Hiding
In programming, data hiding helps us to define the privacy of data from the outside world or to make it distinct from other classes.
Why do we hide data? It is because we need to create several levels of accessing an object's data and prevent it from accidental modification. In addition, hiding or setting up privacy levels can be done for functions too. While in OOP, the data inside the classes can be defined as public, private, or protected.
Private data or functions are the ones that cannot be accessed or seen from outside the class, while public data or functions can be accessed from anywhere, and the Protected data or functions act like public but should not be accessed from outside.
Abstraction of Data
In Python, classes use the concept of abstraction. In addition, a class encapsulates the relevant data and functions that operate on data by hiding the complex implementation details from the user, as the user needs to focus on the actions of a class, instead of how it does the action.
Encapsulation
This is an important reason for the existence of an object. The encapsulation is typically what bounds all the things related t objects such as their data, privacy, functions, and so on. In Encapsulation, data and functions belonging to a class are brought together.
Inheritance
This refers to defining a set of core properties and functions in one place and then re-using each and every one of them by inheriting the class in which they are defined.
In Python, Simple, Multiple, and MultiLevel Inheritance are very well supported. You will learn this in the tutorial on inheritance.
Polymorphism
The word Polymorphism, is Poly + Morph, meaning "many forms”. It is the property of any function or operator that can behave differently depending upon the input that they receive from a user.
There are two forms in which Polymorphism can be achieved. They are:
- Function Overloading
- Operator Overloading
Function Overloading
Functions can be made to act differently using function overloading in OOP. In other to do this, we have to create different functions with the same name having, but with different parameters. e.g. suppose a function add(), which adds all its parameters and returns the result. This can be defined in Python like this:
def add(a, b):
return a + b;And it is can execute function calls like this:
>>> add(4,5)
From the example above, the add function will take 2 numbers as input, but, if we decide to add 3 numbers at once or 4 numbers. So, in OOP you can simply define the function add once again, this time with 3 parameters. This mechanism is referred to as Function Overloading.
# to add 3 numbers
def add(a, b, c):
return a + b + c;
# to add 4 numbers
def add(a, b, c, d):
return a + b + c + d;From the example above, let’s call the add() function with 2, 3, and 4 parameters. you will notice the fact that the add() function has multiple forms.
Operator Overloading
Some of the operators we have include addition, Division, Multiplication, and so on. The Python language can read operators differently depending upon the situation. Check out the example below:
>>>print(2 + 5)It will give you output 7, but doing
>>>print( "hello" + "world")The example above gives an output of “helloworld”. You saw how the + operator performed mathematical addition operation when used with numbers. However, when it is used with strings it performs concatenation.
Also, when used, the multiplication operator acts differently based on the data of the variables with which it is used. Check out the example below:
>>>print( 3*7)Gives, 21, while on string,
>>> print("hello"*3)Output:
hellohellohelloit gives, "hellohellohello".
This is operator overloading example.
