- Home
- HTML
-
CSS
- Introduction of CSS
- CSS Syntax
- CSS Selectors
- How To Add CSS
- CSS Comments
- CSS Colors
- CSS Backgrounds
- CSS Borders
- CSS Margins
- CSS Text
- CSS Lists
- CSS Tables
- CSS Box Model
- CSS Dimension
- CSS Padding
- CSS Border
- CSS Margin
- CSS Outline
- CSS Cursors
- CSS Overflow
- CSS Units
- CSS Visual Formatting
- CSS Display
- CSS Visibility
- CSS Position
- CSS Layers
- CSS Float
- CSS Alignment
- CSS Pseudo-classes
- CSS Pseudo-elements
- CSS Media Types
- CSS Sprites
- CSS Opacity
- CSS Attribute Selectors
- CSS Validation
- CSS3 Border
- CSS3 Gradients
- CSS3 Text Overflow
-
JavaScript
- JS Introduction
- JS Getting Started
- JS Syntax
- JS Variables
- JS Generating Output
- JS Data Types
- JS Operators
- JS Events
- JS Strings
- JS Numbers
- JS If Else
- JS Switch Case
- JS Arrays
- JS Sorting Arrays
- JS Loops
- JS Functions
- JS Objects
- JS DOM Nodes
- JS DOM Selectors
- JS DOM Styling
- JS DOM Get Set Attributes
- JS DOM Manipulation
- JS DOM Navigation
- JS Window
- JS Screen
- JS Location
- JS History
- JS Navigator
- JS Dialog Boxes
- JS Timers
- JS Date and Time
- JS Math Operations
- JS Type Conversions
- JS Event Listeners
- JS Event Propagation
- JS Borrowing Methods
- JS Hoisting Behavior
- JS Closures
- JS Strict Mode
- JS JSON Parsing
- JS Error Handling
- JS Regular Expressions
- JS Form Validation
- JS Cookies
- JS AJAX Requests
- JS ES6 Features
-
jQuery
- jQuery Introduction
- jQuery Syntax
- jQuery Selectors
- jQuery Events
- jQuery Show/Hide
- jQuery Fade
- jQuery Slide
- jQuery Animation
- jQuery Stop
- jQuery Chaining
- jQuery Callback
- jQuery Get/Set
- jQuery Insert
- jQuery Remove
- jQuery CSS Classes
- jQuery Style Properties
- jQuery Dimensions
- jQuery Traversing
- jQuery Ancestors
- jQuery Descendants
- jQuery Siblings
- jQuery Filtering
- jQuery Ajax
- jQuery Load
- jQuery Get/Post
- jQuery No-Conflict
-
PHP
- PHP Introduction
- PHP Install
- PHP Syntax
- PHP Comments
- PHP Variables
- PHP Echo / Print
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Strings
- PHP Constants
- PHP Operators
- PHP If...Else...Elseif
- PHP Switch
- PHP Loops
- PHP Functions
- PHP Arrays
- PHP Superglobals
- PHP Date and Time
- PHP Include
- PHP File Handling
- PHP File Upload
- PHP Cookies
- PHP Sessions
- PHP Filters
- PHP Callback Functions
- PHP JSON
- PHP Exceptions
- PHP What is OOP
- PHP Classes/Objects
- PHP Constructor
- PHP Destructor
- PHP Access Modifiers
- PHP Inheritance
- PHP Abstract Classes
- PHP Interfaces
- PHP Traits
- PHP Static Methods
- PHP Namespaces
-
SQL
- Introduction to SQL
- SQL Create Command
- SQL ALTER Command
- SQL Truncate Drop Rename
- INSERT SQL command
- UPDATE SQL command
- DELETE SQL command
- SQL COMMIT command
- SQL ROLLBACK command
- SQL GRANT and REVOKE Command
- SQL WHERE clause
- SQL LIKE clause
- SQL ORDER BY Clause
- SQL Group By Clause
- SQL HAVING Clause
- SQL DISTINCT keyword
- SQL AND OR operator
- SQL Constraints
- SQL Functions
- SQL JOIN
-
Python
- Getting started with Python
- Introduction to IDLE
- Python 2.x vs. Python 3.x
- Syntax Rules and First Program
- Numbers and Math Functions
- Python Operators
- Python Variables
- Python Modules and Functions
- Python Input and Output
- Data Types in Python
- String in Python
- String Functions in python
- Lists in Python
- Utilizing List Elements by Iterating
- Deleting List Elements & other Functions
- Dictionaries in Python
- Functions for Dictionary
- Tuples in Python
- Relational and Logical Operators
- Conditional Statements in Python
- Looping in Python
- Define Functions in Python
- Python-Introduction to OOP
- Object Oriented Programming in Python
- Classes in Python
- The concept of Constructor
- Destructors - Destroying the Object in Python
- Inheritance in Python
- Access Modifers in Python
- Types of Inheritance
- Method Overriding in Python
- Polymorphism
- static Keyword
- Operator Overloading Python
- Introduction to Error Handling
- Exception Handling: try and except
- Exeption Handling: finally
- Exception Handling: raise
- File Handling
- Reading and Writing File
- Introduction to Multithreading
- Threading Module in Python
- Thread Object
- Lock Object
- RLock Object
- Event Object
- Timer Object
- Condition Object
- Barrier Object
- __name__ Variable in Python
- Iterable and Iterator
- yield Keyword
- Python Generators
- Python Closures
- Python Decorators
- @property Decorator in Python
- Assert Statement
- Garbage Collection
- Shallow and Deep Copy
- Introduction to Logging
- Configure Log LEVEL, Format etc
- Python Logging in a file
- Python Logging Variable Data
- Python Logging Classes and Functions
- Python MySQL Introduction
- Create Database - Python MySQL
- Create Table - Python MySQL
- Insert Data in Table
- Select Data from Table
- Update data in Table
- Delete data from Table
- Drop Table from Database
- WHERE clause - Python MySQL
- Order By clause - Python MySQL
- Limit clause - Python MySQL
- Table Joins - Python MySQL
-
MongoDB
- MongoDB Introduction
- Overview of MongoDB
- MongoDB vs SQL Databases
- Advantages of MongoDB
- When to go for MongoDB
- Data Modelling in MongoDB
- Is MongoDB really Schemaless?
- Installing MongoDB on Windows and Linux
- Datatypes in MongoDB
- Create and Drop Database in MongoDB
- MongoDB: Creating a Collection
- CRUD Operations in MongoDB
- Data Relationships in MongoDB
- Indexing in MongoDB
- Sorting in MongoDB
- Aggregation in MongoDB
- Data Backup and Restoration in MongoDB
- Sharding in MongoDB
- Java Integration with MongoDB
-
Elixir
- Elixir Overview
- Elixir Environment
- Elixir Basic Syntax
- Elixir Data Types
- Elixir Variables
- Elixir Operators
- Elixir Pattern Matching
- Elixir Decision Making
- Elixir Strings
- Elixir Char Lists
- Elixir Lists and Tuples
- Elixir Keyword Lists
- Elixir Maps
- Elixir Modules
- Elixir Aliases
- Elixir Functions
- Elixir Recursion
- Elixir Loops
- Elixir Enumerables
- Elixir Streams
- Elixir Structs
- Elixir Protocols
- Elixir File I/O
- Elixir Processes
- Elixir Sigils
- Elixir Comprehensions
- Elixir Typespecs
- Elixir Behaviours
- Elixir Errors Handling
- Elixir Macros
- Elixir Libraries
-
TypeScript
- TypeScript Overview
- Install TypeScript
- First TypeScript Program
- Type Annotation
- TypeScript Variable
- TypeScript Data Type Number
- TypeScript Data Type String
- TypeScript Data Type Boolean
- TypeScript Arrays
- TypeScript Tuples
- TypeScript Enum
- TypeScript Union
- TypeScript Any Data Type
- TypeScript Void Data Type
- TypeScript Never Data Type
HTML Styles - CSS
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is an acronym for Cascading Style Sheets. CSS helps you save time and effort. It has the ability to control the layout of numerous web pages at the same time.
What exactly is CSS?
The layout of a webpage is created using Cascading Style Sheets (CSS).
Color, font, text size, spacing between components, how elements are positioned and laid out, what background pictures or background colours are to be used, different representations for different devices and screen sizes, and often more can all be controlled with CSS.
Tip: Cascading refers to the fact that a style given to a parent element will be applied to all children elements within the parent. So, if the body text is set to "blue," all headings, paragraphs, and other text elements within the body will be the same colour (until you specify otherwise)!
Using of CSS
- Inline - when the style attribute is used within HTML elements.
- Internal - a <style> element in the <head> section is used.
- External - by linking to an external CSS file with the <link> element.
Inline CSS
Inline CSS is a style that is applied to a single HTML element.
The style attribute of an HTML element is used in an inline CSS.
The following example sets the text color of the <h1> element to blue, and the text color of the <p> element to red:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1 style="color:blue;">A Blue Heading</h1>
<p style="color:red;">A red paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>Output:

External CSS
For many HTML pages, an external style sheet is required to specify the style. Add a link to an external style sheet in the section of each HTML page:
Consider the following scenario:
Any text editor can be used to create the external style sheet. The file must be saved with a .css extension and must not contain any HTML code.
Example :
The external style sheet can be written in any text editor. The file must not contain any HTML code, and must be saved with a .css extension.
Here is what the "styles.css" file looks like:
“styles.css”
body {
background-color: powderblue;
}
h1 {
color: blue;
}
p {
color: red;
}Tip: Editing the look of a complete website using an external style sheet is as simple as changing one file!
CSS Colors, Fonts and Sizes
We'll show you how to use some of the most common CSS properties here. Later on, you'll discover more about them.
Color: The text color is determined by the CSS color attribute.
Fonts: The font-family CSS attribute specifies the typeface that will be used.
Sizes: The font-size attribute in CSS determines the text size that will be employed.
Example:
Use of CSS color, font-family and font-size properties:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h1 {
color: blue;
font-family: verdana;
font-size: 300%;
}
p {
color: red;
font-family: courier;
font-size: 160%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>Output :

CSS Border
A border around an HTML element is defined using the CSS border attribute.
Tip: Nearly all HTML components can have a border defined.
Example :
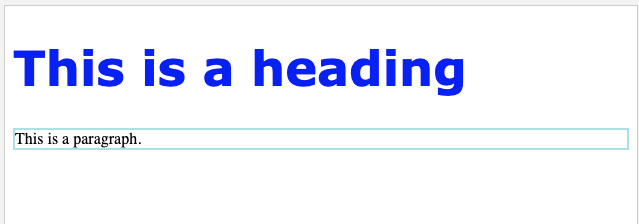
Use of CSS border property:
p {
border: 2px solid powderblue;
}Output :
CSS Padding
The padding (space) between the text and the border is defined by the CSS padding property.
Example :
Use of CSS border and padding properties:
p {
border: 2px solid powderblue;
padding: 30px;
}
CSS Margin
The margin (space) outside the border is defined by the CSS margin attribute.
Example:
Use of CSS border and margin properties:
p {
border: 2px solid powderblue;
margin: 50px;
}
External style sheets can be referred to using either a full URL or a relative path to the current web page.
